What is the MVC Pattern?
The MVC pattern is the primary pattern in software developments which separates the application into three interconnected components. With the help of this developers can understand the codebase easily and help them to maintain with less mess.
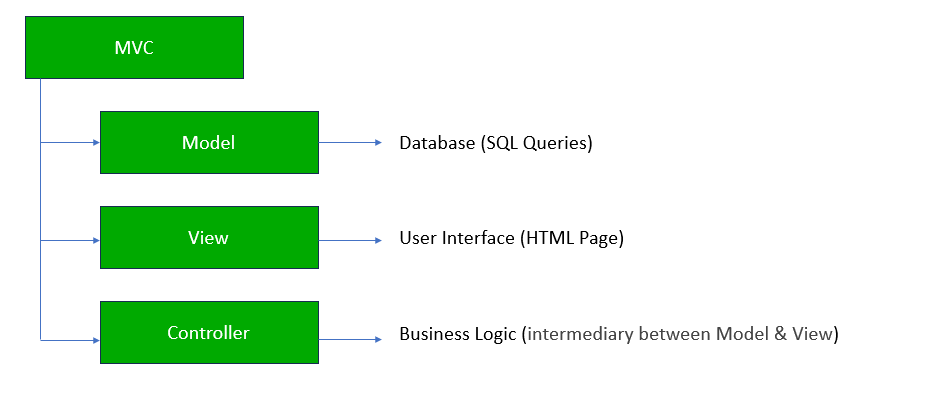
MVC have three components:
- Model
- View
- Controller
- Model: This represents the data layer of your application. The Model is responsible for retrieving, storing, and processing data from the database. It contains the business logic of your application.
- View: The View is responsible for the presentation layer. It’s what the user sees when they interact with your application. It could be an HTML page, a form, or any other UI component that displays data.
- Controller: The Controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It receives input from the user, processes it (sometimes using the Model), and returns the appropriate output to the View. In simpler terms, it handles user requests, manipulates data, and then returns a response.
Why Use MVC?
- Better code management.
- Reuse of different components including models, views, and controllers.
- Better collaboration because different developers work on different parts of the application simultaneously.
- Easy code base management in large-scale projects.
MVC Workflow
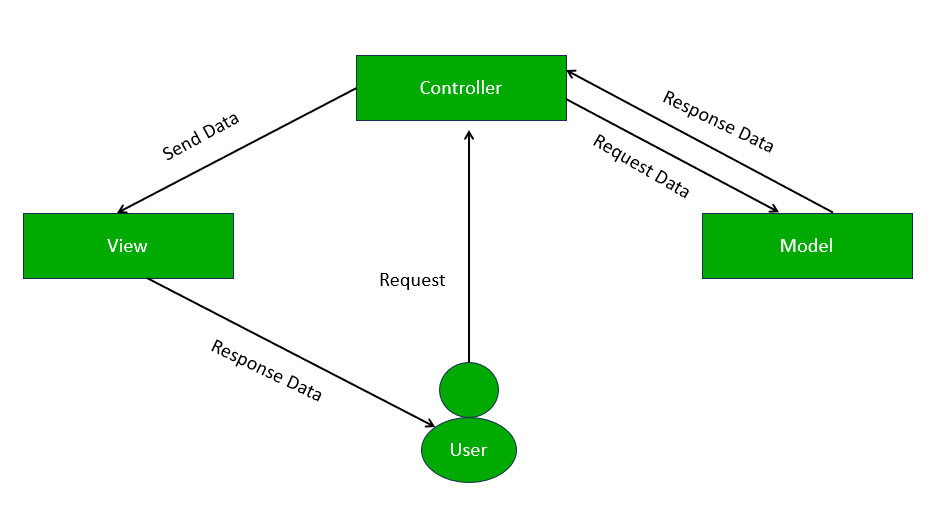
- The user continues that interaction with an application and it will repeat again in that cycle.
- The user interacts with an application with a request for information or for updating a module.
- The controller receives the request, interprets it, gathers necessary information, and creates any requests to the model.
- The model reflects the application with new change requests or gathers requested information.
- The controller then sends the response.
- The view is the use interface of the application. A view collects data from a controller and displays it to the user.
Summary
- Model: It manages data and business logic.
- View: Displays the data for the user while feeding it with user input.
- Controller: Act as a mediator between the View and the Model, where the input of the user gets processed, while in turn updates and modifies the information in the View as well.
This separation of concerns allows for better organization, easier maintenance, and scalability for applications.
Comments (2)
LEAVE A COMMENT
Our Services
Discover our range of professional services designed to meet your needs. We provide expert solutions with precision and excellence to help you achieve your goals.


Awesome Explanation!!!
This is a really informative post! I’ve been using Laravel for a while now, and I appreciate the detailed explanation of the MVC pattern. It definitely cleared up some things for me. Keep up the great work!